Be Smart in How You Staff

An architecture firm is only as good as its people. Here are a few tips for attracting—and retaining—the best in the business.
By Nate Berg
From entry-level interns to top-tier management, the business of architecture relies on smart workers [staff]. To stay competitive and endure an ever-turbulent job market, design firms need to recruit the best and the brightest while holding on to the skilled talent they already have.
Look for Inquisitive Minds
When seeking new talent, New York–based Robert A.M. Stern Architects partner Graham Wyatt, AIA, says firms should look broadly at the candidates’ talents. Architectural ability and design skills are obviously important, but they shouldn’t be the only factors considered. “Look for people who are broadly educated and, beyond that, people who are inquisitive about the world, who are not just one-dimensional,” he says.
Incentive High Performance
Rewarding employees based on the quality of their work will push them to excel and make them feel appreciated. Robert A.M. Stern Architects uses a system as part of a profit-sharing model that, when the firm is in the black, issues an additional bonus to employees based on annual reviews. “The principle of it is important to the culture of our firm, which is to reward people at all levels so they feel that they’re pulling in the same direction,” Wyatt says, “and that’s really essential to our success.”
Respond to Shifts in Supply and Demand
The layoffs during the recession may seem like fresh wounds, but the market has recovered. Demand for architects is high now due to increased work and a limited supply of professionals. “Twenty to 30 percent of the architectural workforce left in the last recession, so the talent pool is much smaller,” says David McFadden, CEO of Consulting for Architects, a staffing agency. Firms need to recognize that it’s a seller’s market. “Architects are just not sitting on a department store shelf anymore.”
Evaluate Routinely
Regular performance reviews are crucial for employers to track progress and for workers to get positive feedback, constructive criticism, and, ideally, a chance to request a raise. Communication is mutually beneficial, but it sometimes doesn’t happen enough. “In some firms, the annual review only happens every two or three years,” says Herbert Cannon, president of consultancy AEC Management Solutions. “That can be demoralizing to employees.”
Be Less Picky, Hire More Quickly
A dearth of architects means employers need to adjust expectations and perhaps lower their hiring standards. The perfect candidate simply might not exist. “There’s still this perception that there’s people available that meet all of your criteria. But in fact there’s not and so you need to make a quick attitude adjustment,” says McFadden. To top it off, the limited supply is in such demand—the candidates you want may be under consideration by other firms. McFadden suggests acting quickly: “Shorten the time from receiving a résumé to scheduling an interview to making an offer. … You have to be quick; otherwise you’re going to lose out to a firm that is.”
Honor Loyalty
Firms need to know how to hold on to what they’ve got. That was easier during the recession when many architects were happy to have any job. But now that things have turned around and opportunities are opening up, employers need to do more to keep their workers from perusing the job boards. McFadden says firms should increase compensation for the people who stuck with them during the recession, and even more so for those who saw years pass by without a raise.
by Nate Berg for Architectmagazine.com*
*This article was not written for The CFA Blog. This article was written for Architect Magazine.com and reposted by CFA for the CFA Blog.
Editors note: Obviously, we contributed to this article, and agree with the points Nate makes. Do you agree that the hiring trend favors the applicants?
Search Careers Request Talent Join Mailing List“Where Are The Qualified Architects?”

Employers Ask. They All Got Jobs.
6 Crucial Ways to Repopulate Your Workforce
Introduction
Unemployment rates are still uncomfortably high across the nation, there is a misperception that architectural talent must be plentiful, but for specific experience, the exact opposite is true. The shortage is so acute that it has been associated with a rise in offshoring, a bidding war and comparisons to college recruiting. To secure the architecture talent they need, hiring managers must adopt a competitive hiring strategy or lose to someone who does.
Architects had to get even more creative after the economic recession that began around December 2007. The built-in versatility from their studies in areas such as civil engineering, math, art history, and physics positioned them well for thinking outside the box. Jumping ahead seven years, the demand for architectural talent in the wake of the recession has re-stabilized, but talent availability lags behind. No hiring firm could have possibly predicted this rapid shift. To remedy the imbalance between supply and demand, hiring firms must shift their perception of what is viable and consider potential candidates on more realistic criteria.
Supply and Demand
Within the last 10 years, supply and demand in the architecture industry have moved in opposite directions. Uncertainty about capital access discouraged building development, leading to dormant projects and a lack of ambition in both the commercial and residential markets. In 2012, a study by Georgetown University revealed that architecture graduates had experienced the highest rate of unemployment (13.9%) when compared to other fields. Prior to the recession, this problem was not nearly so pronounced.
The Recession’s Effect
The poor economy challenged architects to get creative. According to the Department of Labor, 39,900 jobs were lost in 2010 alone. Architects were forced to think flexibly in order to sustain a livelihood and many did. For example, take 26-year-old architect Natasha Case: she was laid off from a prestigious position at Walt Disney Imagineering. Within a year, Case developed a homemade mobile ice cream business with a friend. Flavors were inspired by architecture. One such flavor was the “Frank Behry,” named after renowned architect Frank Gehry. The startup was such a hit that Case’s former employer, Walt Disney Imagineering, became a customer.
Case is not the only person who resorted to new endeavors during the recession. After years of uncertainty, architects have settled into new careers both in and outside of the industry, leaving the talent pool depleted.
Demand is Rapidly Growing
As the architecture industry attempts to bounce back from economic instability, the landscape has changed significantly. According to MNI News, hiring firms in New York, Los Angeles, and North Carolina report explosive growth; the American Institute of Architects released a billing index in August 2014, showing its highest growth rate since 2007. There are no signs of this pattern slowing.
Industry spending is projected to increase by 10 percent for non-residential construction in 2015. Kermit Baker, chief economist at the American Association of Architects, attributes this growth to more capital access and recovering business confidence.
Institutional projects, which were sluggish in early 2014, are generating growth as well, with public, private and charter school projects popping up in New York City, Long Island, and beyond. Better access to capital has allowed for the renewal of projects that were once dormant, and for the launching of new ones. The Housing Studio, an 18-year-old firm in Charlotte, North Carolina, is billing at its highest rates.
According to the Federal Reserve’s economic forecast, growth is expected to rise 3 percent in the second half of 2014, followed by another 3 percent in 2015. At the same time, the national unemployment rate is projected to fall to 5.5 percent in 2015. Design projects are regenerating, demand snowballing nationally, and architectural demand outpaces supply.
The Talent Pool
Like Natasha Case, many architects have scattered into new industries since the recession. Architecture graduates have been forced out of the field due to a lack of opportunities and inadequate levels of experience.As many hiring firms know, several factors must fall into place for talent to be hired for a project. Candidates are expected, at a minimum, to be proficient in design software, have at least three to seven years of experience in a specific type of work, be eligible to work in the U.S, and be a good cultural fit. The rise in both residential and commercial design projects in 2014 qualified architects, who are still in the talent pool, simply cannot meet the demand.
On top of this, federal and state laws provide a slew of other obstacles for hiring firms to secure the right candidates. Even small firms must comply with the requirements laid out by the Affordable Care Act and the Department of Labor and Homeland Security. Further complications arise when determining exempt vs. nonexempt employees, contractors and overtime eligibility. Considering this myriad of complications, it is no surprise that firms are experiencing an imbalance of supply and demand.Aside from this, cultural changes have caused Millennials to leave their firms after an average of just three years. This puts an extra layer of pressure on firms to continuously cycle through the recruitment process. Retention levels have dipped due to this shift toward a freelance-style career.
In combination, these factors lead to significant stress and a continuous lack of stability at firms, who must constantly process recruitment materials and decide on new candidates. A simple attitude adjustment by hiring firms is necessary for the industry to regain its economic footing. This does not refer to a lowering of standards but rather an expansion in considerations during the hiring process.
In Order to Compete for Quality Talent, Hiring Firms Must Be More Flexible in 6 Crucial Areas:
1. Experiential Requirements
Considering the sluggish pace at which design projects progressed in recent years, newer architects were unable to acquire extensive experience in various areas. With larger commercial projects handed off to established architects, those with less experience are continuously overlooked.
2. Cultural Fit
While a person’s character and their ability to mesh with current company values are important, the decision to hire should primarily be determined by the candidate’s ability to execute the design. Assessing perfect cultural fit is generally a matter of opinion, best made flexible during times of talent shortages.
3. Compensation
Considering the level of competition currently face by hiring firms who are in need of talent, flexibility in compensation is crucial. Approaching candidates confidently with a reasonable figure will motivate them and assure them that they are in the right place.
4. Hiring Time
Architects are at an advantage as the industry currently stands. When the correct candidate is found, hiring firms should work to reduce the time between the initial meeting, and the extension of an offer; under lengthier circumstances, architects may move on to other available firms.
5. Employment Duration
While it may be frustrating for both firms and architects to be floating in a sea of uncertainty, this post-recession period of adjustment are unavoidable. It’s worth considering a candidate regardless of the amount of time he or she plans to stay with a firm, and the training time required.
6. Project Placement
In a talent shortage such as this, it may not be feasible to have every employee working as a full-time staff member. While it may sound like a hassle, temporary employees can provide the extra energy burst needed to push a project beyond original expectations. These employees could also serve as a more objective third party with unique backgrounds and perspectives while stabilizing the peaks and valleys associated with architectural practice.
Conclusion
As projects slowly resume and capital becomes available, a full recovery from the recession is in sight. The final puzzle piece involves architects being reacquainted with hiring firms. At least a few decades will pass before for the talent pool can catch up with demand. With many senior architects out of the game for good, and waves of graduates who’ve yet to mature, this problem won’t diminish anytime soon.In order to bridge the gap, hiring firms must be willing to adapt. If the above changes are implemented, hiring firms will be better able to thrive in the industry’s current climate.
Search Careers Request Talent Join Mailing ListArchitects Billing Index

Firms Report Strongest Billing Since Before Recession
PHILADELPHIA (MNI) – U.S. architects are enjoying the fastest growth in billings since before the recession for their work on a range of residential and commercial construction projects, and expect continued growth in coming months, according to company owners and a trade association.
Architecture firms in Los Angeles, New York, and Charlotte, North Carolina said they have hired more people in recent months and expect to hire again to cope with the extra demand from developers of apartment buildings, retail space and in some cases institutional properties like charter schools.
While some companies have at least doubled their billing and the size of their payrolls since the depths of the recession, most said they have work in the pipeline that suggests even stronger revenue in 2015.
“This is really just getting underway,” said Kermit Baker, chief economist at the American Association of Architects, in an interview. “We are very much in the early innings of what looks to be a healthy recovery.”
The AIA’s monthly index of billing, which in July showed its strongest growth since mid-2007, is expected to show continued strength when the August index is released on Sept. 24, Baker said.
“I don’t think there’s any evidence that August was off that trend line significantly,” he said.
The industry has seen intermittent growth during the last three or four years so the evidence of a sustained upturn is not yet conclusive but the current increase is the strongest since the recession, Baker said.

The growth suggests there will be an upturn in non-residential construction spending of around 10% in 2015, Baker said. He attributes the upswing to improving business confidence and better access to capital.
“Businesses are finally at a stage where they are comfortable reinvesting in their facilities, and comfortable that the economic upturn is going to be sustained,” he said. “They are seeing sufficient demand to justify reinvestment.”
The greater availability of financing is allowing the restart of construction projects that stalled several years ago because of a tight credit environment after the recession.
“Financing has begun to ease up a little bit,” Baker said. “Surprisingly strong numbers of firms are saying they are now working on projects that they had begun three or four years ago, but stopped work and now they have come back.”
Even the market for design of institutions such as schools is coming back after a period when it was hurt by a decline in local government tax revenue.
“The last couple of months we have seen very strong numbers on the institutional side, which would suggest that construction activity moving into 2015 will begin to pick up,” Baker said.
The higher demand for institutional work has been seen in New York City where Caples Jefferson Architects is designing schools for both public and private-sector clients, as well as undertaking more work on residential projects.
“There are lots and lots of charter school construction going on right now as well as public construction,” said Sara Caples, president and principal of the firm in Long Island City.
Caples said demand for her firm’s services is at its strongest for at least five years, and that billing in the last few months has been about double its level of a year earlier. And in a sign that billings will growth further, she said she has had a “flood” of requests for proposals in recent months, and is responding to an unusually large number of them.
“We throw out a lot of requests for proposals if we don’t think we have a strong chance, and we’re still putting out a major proposal every week or so, which is just extraordinary,” she said.
Current projects include a 20,000 square-foot charter school in the Bronx, and a 40,000 square-foot charter school plus a 12-unit residential component in Manhattan, she said.
Residential developments are facilitating the construction of associated institutional projects because of the strong retail market in New York, Caples said.
“The market is strong enough that the residential makes it viable to build the six-story school on quite a challenging site,” she said. “The 12 residential units will allow them to pay off the mortgage very rapidly. The residential market seems to be the little engine that’s financing quite a lot of things.”

The eight-person firm already is two architects bigger than it was at the start of 2014, and may add more, despite an extremely selective hiring policy, if it takes on just one or two projects, she said.
The growth is being fueled by easier access to finance, which is helping not only to revive dormant projects but to launch new ones, Caples added.
“That’s what’s different about this,” she said. ‘Now, people are actually making new deals with their financiers that haven’t been kicking around forever.”
And she said her firm’s current growth seems to be representative of the market as a whole. “Most of the people that we talk to seem to be experiencing similar patterns,” she said.
In Charlotte, North Carolina, The Housing Studio, an architecture firm specializing in multi-family housing projects around the East Coast between Philadelphia and Charlotte, and in the Denver, Colorado area, is seeing an “explosion” in growth, said President Chuck Travis.
He said the company is billing about $3 million annually or more than three times the level during the recession. Its 28-strong work force is now about twice its traditional size, and four times its level at the low point of the recession. Travis said he’s looking to hire four or five more architects.
Travis said the growth is unprecedented in the company’s 18-year history. “It’s exponential growth in a two-year time frame,” he said.
He attributed the upswing to increased demand for rental housing in the walkable or transit-oriented urban areas that are favored by the “millennial” workers who eagerly sought by developers across the country.
That sector of the population is less interested in housing as an investment than was the previous generation, and prefers the flexibility of rented accommodation, he said, predicting continued growth.
“We’re not showing any signs of slowing down,” he said.
The demand for downtown living is also being seen in a three-square-mile area of Los Angeles, where 6,000 residential units are under construction and another 14,000-16,000 units are being planned, according to Simon Ha, a partner with TSK Architects.
That is creating more work for firms like TSK which is billing 30% more than it did a year ago, and has hired four architects this year for a total of 10, Ha said. And demand is stronger than it was in the pre-recession years of 2006-2007.
The construction boom, which he said is being fueled by investment from China, has resulted in land prices in the downtown area jumping to around $400 a square foot from $250-$300 two years ago. Land near LA’s Staples Center is now selling for about $600 a square foot, or about double its level two years ago, he said.
With a booming population of single people demanding housing in previously desolate urban areas like downtown LA, there are big opportunities for companies like TSK which has increased its billing for residential design to 70% of its total, Ha said.
By
Search Careers Request Talent Join Mailing ListAIA Comp Survey: Minimal Salary Increase

Lingering impact from the Great Recession slows gains in salaries
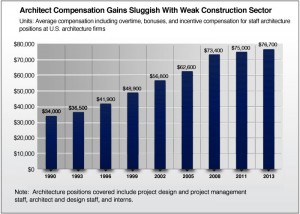
Over the last several years, most architecture firms have benefited from a general improvement in the economy as well as in the construction sector. Revenue at architecture firms increased almost 11 percent in 2012 from 2011 levels, according to U.S. Census Bureau figures, and firm payrolls have followed suit. But this modest improvement in business conditions has done little to lift compensation levels at firms. Between 2011 and 2013, average total compensation for architecture positions—including base salary, overtime, bonuses, and incentive compensation—increased only slightly over 1 percent per year, barely more than the average increase in compensation between 2008 and 2011, when the construction sector was still in steep decline.
Even this modest 1 percent increase in average architect compensation may overstate the experience of the typical architect during this period. Average compensation depends on the mix, by experience levels, of positions reporting. Since many less experienced architecture positions were eliminated during the downturn, current average compensation may reflect a higher share of more experienced (and more highly compensated) positions. Regardless, while average compensation for architecture positions increased a mere 0.7 percent per year compounded between 2008 and 2011, growth increased to only 1.1 percent per year between 2011 and 2013 (Exhibit 1.1).
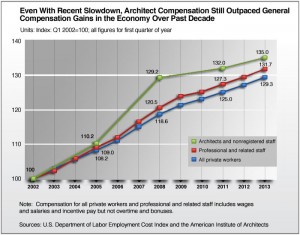
Architecture staff compensation tends to be more volatile over the business cycle than compensation for most other occupations. Over the past decade, compensation gains for architecture positions have more than kept pace with compensation across the entire economy. Architecture compensation increased 35 percent between early 2002 and early 2013, compared to just under 32 percent for all professional and related staff (typically defined as white-collar workers such as lawyers, accountants, etc.), and just over 29 percent for all private-sector workers (Exhibit 1.2).
Compensation levels vary by firm size
Historically, large architecture firms have offered higher levels of compensation. These comparisons are more difficult for more senior positions because job responsibilities are difficult to compare across firms of different sizes. However, this disparity exists even for positions with relatively standard job descriptions such as Intern 1 or Architect 1.
At firms with fewer than 10 employees, Intern 1 compensation averaged 10 to 15 percent below national averages. At firms with more than 250 employees, Intern 1 compensation averaged more than 10 percent above the national average. A similar pattern held for Architect 1 positions: about 10 percent below the national average at firms with fewer than 10 employees, and almost 10 percent above the national average at firms with 250 or more employees.
Staff turnover and fringe benefits reflect improvement
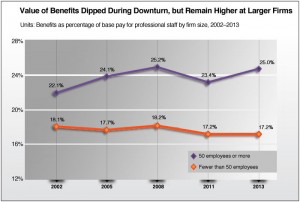
Another sign that business conditions have stabilized across the profession is that benefits offered to employees have begun to modestly improve at many firms. While declining between 2008 and 2011 as firm revenues eroded, they rebounded modestly by 2013, with benefits packages averaging 18 percent of base salaries for professional staff. Benefits have bounced back faster at larger firms and remain significantly higher than those offered by smaller firms (Exhibit 1.3).
Recent Related:
AIA Compensation Survey: Architect Compensation Stagnant
Reference:
Purchase the 2013 AIA Compensation Report
New for 2013: Architect Compensation by Metro Area
Back to AIArchitect August 9, 2013
Go to the current issue of AIArchitect
5 Questions You Should Never Ask in a Job Interview

Could these words be costing you your dream job?
By Catherine Conlan, Monster Contributing Writer
Hiring managers and HR pros will often close out a job interview by asking an applicant if he or she has any questions themselves. This is a great opportunity to find out more about the job and the company’s expectations, but you can’t forget that the interviewer hasn’t stopped judging YOU. Here are 5 questions that can make a bad impression on your interviewer, scuttling your chances for getting the job.
1. “When will I be promoted?:
This is one of the most common questions that applicants come up with, and it should be avoided, says Rebecca Woods, Vice President of Human Resources at Doherty Employer Services in Minneapolis. “It’s inappropriate because it puts the cart before the horse.” Instead of asking when the promotion will occur, Woods says a better approach is to ask what you would need to do to get a promotion.
2. “What’s the salary for this position?”
Asking about salary and benefits in the first interview “always turns me off,” says Norma Beasant, founder of Talento Human Resources Consulting and an HR consultant at the University of Minnesota. “I’m always disappointed when they ask this, especially in the first interview.” Beasant says the first interview is more about selling yourself to the interviewer, and that questions about salary and benefits should really wait until a later interview.
3. “When can I expect a raise?”
Talking about compensation can be difficult, but asking about raises is not the way to go about it, Woods says. So many companies have frozen salaries and raises that it makes more sense to ask about the process to follow or what can be done to work up to higher compensation level. Talking about “expecting” a raise, Woods says, “shows a person is out of touch with reality.”
4. “What sort of flextime options do you have?”
This kind of question can make it sound like you’re interested in getting out of the office as much as possible. “When I hear this question, I’m wondering, are you interested in the job?” Beasant says. Many companies have many options for scheduling, but asking about it in the first interview is “not appropriate,” Beasant says.
5. Any question that shows you haven’t been listening.
Woods said she interviewed an applicant for a position that was 60 miles from the person’s home. Woods told the applicant that the company was flexible about many things, but it did not offer telecommuting. “At the end of the interview, she asked if she would be able to work from home,” Woods says. “Was she even listening? So some ‘bad questions’ can be more situational to the interview itself.”
With the economy the way it is, employers are much more choosy and picky, Beasant says. Knowing the questions to avoid in an interview can help you stand out — in a good way.
Housing on the Rebound: Is it Better to Rent or Buy?

Unlike the stock market, which is setting at record highs, the housing market has yet to recover from the depths of the last recession. While real estate sales and prices are trending higher and are clearly better off than they were a few years (or even months) ago, a full recovery is still far off.
That’s not necessarily a bad thing, since it gives more people more time to take advantage of still low prices and interest rates. Nor is it a good thing, since it means as much as one-third of current homeowners are still underwater with their mortgages (eg. they owe more than the property is worth).
But with prices up, inquiries on the rise, and the spring selling season in full gear, it remains to be seen how this uptrend will play out.
For this installment of Investing 101, Shari Olefson, noted real estate attorney and author of the new book Financial Fresh Start, walks us through the basics of renting versus buying when it comes to making the investment of a lifetime.
1) Follow the “Rule of 15”
Before you make the decision to rent or buy, Olefson offers this rule of thumb: “If you can buy a home in your area for less than 15-times what your annual rent is, than financially it makes much more sense to buy than to rent.”
For example, if you pay $2,000 a month in rent (or $24,000 a year), she says the basic buy-rent cutoff price would be $360,000.
However, she warns that if rental rates in your area are abnormally high or the home you are looking at will need repairs, you must factor that in. Of course, she says “this is only one of several factors to consider,” but adds it is still “a great line in the sand” for narrowing down your initial search.
2) Determine What You Can Afford
Olefson says affordability is another key variable to consider. As a rough guideline, she suggests looking at properties that cost no more than 2.5 to 3 times your annual income on housing.
More…Even if you wanted to spend more, she says the mortgage market has changed drastically and financing requirements are much more strict.
“How you look on paper, what your credit looks like, and do you have the 20% down payment,” are also going to be factors of affordability to consider, as will your employment history.
3) Market Conditions
Whether you rent or buy, the laws of supply and demand certainly apply to housing prices. Right now, Olefson says for a number of reasons, there are simply fewer houses for sale than usual.
“We have four months worth of inventory right now, normally we have over six months,” she says, “that’s about a 25% decrease from this time last year, which is huge and what is driving those prices up.”
To be fair, she conceded part of the reason there are so few listings is because so many sellers are unsure about the market right now and whether or not they want to be in it. Still you have to be careful since national statistics smooth over some of the big statistical differences that vary from market to market, such as foreclosure and unemployment rates.
4) When to Become a Tenant Again
“The same formulas apply,” Olefson says, but that is really “a lifestyle feature” type of question; such as whether or not you may be moving or retiring in the near future. Even so, she says it’s a good idea to look at the local market and familiarize yourself with prices and rents and then run the numbers to see if ”it makes more sense to rent or to own your own home.”
Watch video at source Yahoo Finance
AIA/NCARB Survey Shows Rosier Picture for Emerging Professionals
More interns are employed and getting licensed than during the throes of the recession. Read article http://www.aia.org/practicing/AIAB098254
What’s up, dock? Council approves Pier 57 restoration
The City Council has unanimously approved plans to redevelop the historic Pier 57 at 15th Street and the Hudson River, turning the eyesore into an urban, cultural and retail hub.
The approval clears the way for construction to begin at the pier, which has served as a dock for ocean liners, a former MTA bus depot and a holding pen for rowdy protesters arrested at the 2004 Republican National Convention.

WITHOUT ‘PIER’: An artist’s rendering of Pier 57 after a City Council-approved restoration that will create 425,000 feet of retail space.
Calling it “a major victory for Manhattan’s West Side community,” Council Speaker and mayoral hopeful Christine Quinn said the pier will provide “a new, sorely needed source of revenue” for the Hudson River Trust, which oversees the pier.
“Soon they will transform Pier 57 from an unused waterfront space into an innovative hub, a culture of recreation and public market activity, all located within a restored historic structure,” said Quinn, whose district encompasses the pier.
The plan calls for creating roughly 425,000 square feet of retail and restaurant space built from re-purposed shipping containers, designed by Young Woo & Associates — the same firm that designed Dekalb Market in Brooklyn, also built from old shipping containers.
It will be an “incubator for cutting-edge local and international brands and merchants,” the company said.
It will also feature an amphitheater and a marketplace area made from old airplane fuselages and 160-square-foot “incuboxes” — small spaces for local merchants, artists and start-up companies.
There will also be educational components, such as cooking schools, art galleries, photography labs and music-recording studios. The Tribeca Film Festival will use the 100,000 square feet of outdoor space as a permanent venue.
A 141-slip marina and water-taxi landing space will surround the pier. Construction will begin in October, the company said.
The approval comes after years of wrangling by developers and community activists and after a more elaborate design — a $330 million proposal from real-estate developer Douglas Durst — was killed in favor of the less expensive plan offered by Woo’s company.
The now rusted pier was built in 1952 from three concrete slaps floated down the Hudson River.
“Today’s approval brings us one step closer to transforming Pier 57 into a recreational, cultural and retail center that will provide yet another great destination for the Hudson River Park community,” Hudson River Park Trust President and CEO Madelyn Wils.
Via NY Post [email protected]
Architecture jobs start to bounce back
Online job ads for architects up 20% over year
 Online job advertisements for architects rose 20 percent during the last 90 days compared to the same time period in 2012, according to Wanted Analytics, a firm that tracks online job ads. There were a total of more than 16,000 architect jobs advertised in the past 90 days.
Online job advertisements for architects rose 20 percent during the last 90 days compared to the same time period in 2012, according to Wanted Analytics, a firm that tracks online job ads. There were a total of more than 16,000 architect jobs advertised in the past 90 days.
New York, Los Angeles, Washington D.C., San Francisco and Houston topped the list of metropolitan areas with the most job ads for architects.
“Autodesk AutoCAD” was the most commonly required skill in architect jobs. In the past 90 days, 5,500 jobs required CAD skills, representing about 35 percent of all hiring demand.
The most commonly required skills in architecture jobs include:
Autodesk REVIT Architecture
Oral and written communication skills
Detail oriented
Self-starting/self-motivated
Project management
Organizational skills
Bentley MicroStation
Microsoft Office
Adobe Photoshop
Temporary hiring takes center stage
U.S. temporary employment jumped by 20,300 jobs in March, compared with the previous month, and the year-over-year growth rate ticked up, according to seasonally adjusted numbers released today by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. In addition, the number of temp jobs added in February was revised upward by 22,000 jobs.
Year-over-year growth in temp jobs had been decelerating since November. However, the number of temp jobs rose by 6.4 percent year over year in March, up from the 5.3 percent increase in February.
Further, the U.S. temp penetration rate rose to 1.94 percent in March from 1.93 percent in February.
However, the U.S. added fewer jobs overall in March than February. Total non-farm employment rose by 88,000 jobs in March compared with an increase of 218,000 in February – Sending a clear signal that firms are exercising caution, temporary hires outpaced permanent hires for the same period.
The U.S. unemployment rate still fell to 7.6 percent in March from 7.7 percent in February. The college-level unemployment rate, which can serve as a proxy for professional employment, was unchanged from February at 3.8 percent.
In other industries, construction added 18,000 jobs in March. The BLS reported construction has added 169,000 jobs since September.
Click on the chart below to enlarge.
Click on the chart below to enlarge.

This post is a composite of articles from Staffing Industry Analysts and AIA.org websites
So you want to be an architect?
May I ask why?
Aah architecture. The grand old profession of Wright, Sullivan, Mies and Kahn. The ability to shape cities with one’s own hands, to change lives and alter the course of history. To be Howard Roark of the Fountainhead, dreaming of blowing up your own creation because the client, a necessary evil of the profession, doesn’t share your noble vision.
So very romantic.
And so very wrong.
In the last five years the profession has shed about 60,000 jobs. They’re not coming back. Firms lucky enough to have a backlog of work make up the manpower shortage through technology. Profit margins, traditionally minute in the best of times are non-existent. Consolidation of mid-large size firms is rampant and sole-practitioners are an endangered species. The construction industry is not far away from engulfing architects in the construction process because architects use building information and drawing technologies like CAD, Revit and BIM. We’ve been commoditizing the profession for the last 20 years. That tide is not turning.
Our colleges and universities still eschew teaching the business of architecture, and graduates are ill prepared to deal with the realities of a profession in decline. And don’t dare ask them to draw. A pencil? What’s that?
Then of course there are the clients. The noble benefactors who embrace the architect for his vision, his ability turn their dreams into reality! More likely they’ve shopped around, solicited ten proposals then negotiated two or three firms down to the coveted 3-4% of construction cost fee that fits so well into their bottom line. And the architects fight tooth and nail to see who’ll reach the bottom first. Work is work.
Here’s my advice. Architecture, in its most pure form, is an art that few can understand, enjoy and appreciate. It is exhilarating.
It is not nor should it ever be a job!
It shouldn’t be bought and sold. Be passionate about all design. Architects are inherently creative. Pursue creative collaboration with other design professions. Cross pollinate. Design objects, think creatively at all times and tell everyone you meet that design matters. But practice “architecture” for yourself. Design spaces for yourself. Live in them, work in them, and dream in them. Don’t sell your ideas, your soul, your heart, to anyone. Be selfish because they don’t get it.
If you have to find another way to support yourself.
I’m sure Starbucks is hiring.
Robert Vecchione is an architect/designer and principal of the multidisciplinary firm Cobrooke Ideas-Architecture-Design (www.cobrooke.com)