Tag archives for: design

Introduction
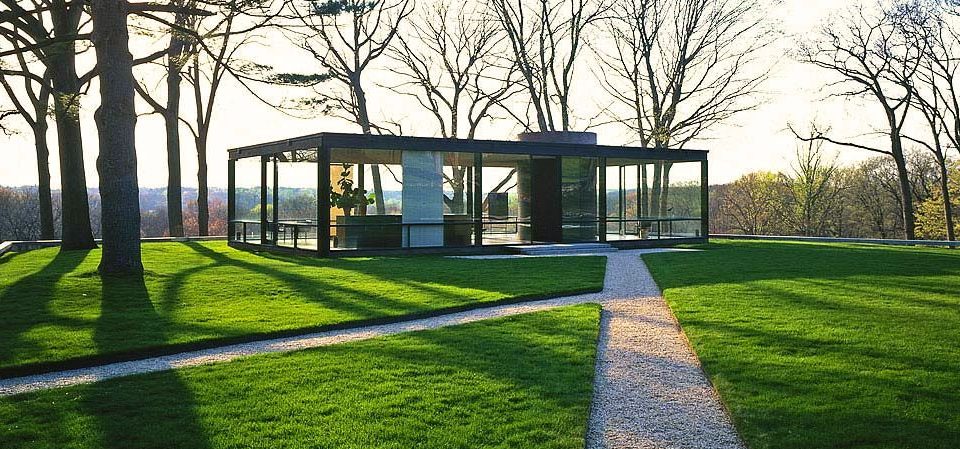
Philip Johnson’s Glass House is a timeless architectural masterpiece renowned for its minimalist elegance and groundbreaking design. Constructed in 1949, this iconic structure was ahead of its time, yet sustainability and energy efficiency were not focal points in the mid-20th century. In this blog post, we’ll explore modern sustainable materials and energy-efficient measures that could be applied today to qualify the Glass House for Platinum LEED Certification—boosting its appeal in the eyes of contemporary environmentally-conscious audiences.
1. Solar Panels and Green Roofing: Harnessing Clean Energy
One of the most influential advancements in sustainable architecture since 1949 is the integration of solar panels and green roofing systems. With today’s highly efficient and cost-effective solar technology, it’s now possible to generate clean energy from the sun. We can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and overall energy consumption by installing solar panels on the Glass House’s roof and surrounding landscape. Incorporating a lush green roof covered in vegetation provides natural insulation and helps reduce stormwater runoff, further enhancing the building’s thermal performance.
2. Advanced Glazing and Insulation: Energy Efficiency at Its Best
The Glass House was an innovative structure for its time, featuring glass walls. However, with the advancements in modern glazing and insulation technology, energy efficiency has reached new heights. High-performance, low-emissivity (Low-E) glass now allows for optimal temperature control by reducing heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter. This, combined with triple-glazed windows and advanced framing materials, enhances insulation and creates a comfortable indoor environment while minimizing the need for excessive heating and cooling.
3. Smart Building Systems: Efficiency in Every Corner
Today, smart building systems offer precise control over various aspects, including lighting, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), and other utilities. Integrating these systems into the Glass House ensures real-time energy use monitoring and adjustment. Features like occupancy sensors, automated shading systems, and energy-efficient LED lighting optimize resource usage and maintain the Glass House’s aesthetic appeal.
4. Sustainable Building Materials: Eco-Friendly Choices
Achieving LEED Platinum certification requires the use of sustainable building materials. The Glass House could be retrofitted with less environmentally impactful materials, such as reclaimed wood, recycled steel, and non-toxic finishes. Additionally, sourcing these materials locally further reduces transportation emissions and supports the local economy.
5. Rainwater Harvesting and Water Efficiency: Resource Conservation
Incorporating rainwater harvesting systems and water-efficient fixtures further enhances sustainability. Capturing rainwater for irrigation and non-potable uses reduces the demand for municipal water supplies. Moreover, including low-flow toilets, faucets, and water-efficient landscaping minimizes water consumption.
Conclusion
Philip Johnson’s Glass House, a 1949 architectural gem, is still captivating with its timeless design. However, with today’s advancements in sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies, we can elevate it to Platinum LEED Certification status. By embracing solar panels, green roofing, advanced glazing, smart building systems, sustainable materials, and water efficiency measures, the Glass House preserves its historical significance. It stands as a symbol of sustainability and innovation. This reimagined Glass House is a testament to harmonizing timeless design with cutting-edge environmental stewardship—an alluring combination for modern eco-conscious enthusiasts.
Consulting For Architects, Inc. Placement
Helping architects, interior designers, and building design professionals find better career opportunities nationwide every day since 1984. Send your resume and portfolio to [email protected]
Architecture: Sustainability Revisited
|
architecture, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, EnergyEfficiency, GreenBuilding, HistoricPreservation, InnovationInDesign, LEEDCertification, ModernDesign, PhilipJohnsonGlassHouse, SolarPower, SustainableArchitecture, SustainableMaterials
|

Biophilic design is a fascinating and increasingly influential approach in architecture and interior design that seeks to incorporate natural elements and patterns into built environments. It emphasizes the connection between humans and nature, aiming to improve well-being, creativity, and productivity. Your blog could delve into various aspects of biophilic design, such as:
1. Principles of Biophilic Design: Explain the core principles of biophilic design, including incorporating natural light, using natural materials, creating indoor greenery, and integrating water features.
2. Case Studies: Highlight real-life examples of buildings or spaces that have successfully embraced biophilic design principles. Showcase the impact of these designs on occupants’ experience and the overall aesthetics.
3. Health and Well-being Benefits: Explore biophilic design’s psychological and physiological benefits, such as reduced stress, increased focus, and enhanced air quality.
4. Biophilic Design in Urban Environments: Discuss how biophilic design can be adapted and integrated into urban settings where natural elements may be limited.
5. Cultural and Historical Context: Examine how different cultures and historical periods have embraced biophilic elements in their architectural designs.
6. Sustainability and Biophilic Design: Explore the connection between biophilic design and sustainable practices, including energy efficiency, reduced waste, and ecological restoration.
7. Innovative Biophilic Technologies: Showcase emerging technologies that enable architects and designers to incorporate biophilic elements creatively.
8. Biophilic Design Challenges: Address potential challenges and considerations when implementing biophilic design, such as maintenance of greenery, weather conditions, and cost-effectiveness.
9. Public Spaces and Biophilic Design: Discuss how biophilic design can transform public spaces like parks, plazas, and community centers to create more inviting and harmonious environments.
10. Future Trends: Explore the evolving trends in biophilic design and how architects and designers are pushing the boundaries to create innovative and sustainable spaces.
By diving into the world of biophilic design, your blog can provide valuable insights and inspiration to architects and designers looking to create more harmonious and nature-inspired spaces.
In a world where our interactions with the natural environment are increasingly limited, biophilic design emerges as a transformative force within architecture and design. It bridges the gap between the built environment and the beauty of nature, reminding us of the intrinsic connection we share with the world around us.
As architects and designers continue to explore and embrace biophilic principles, they usher in a new era of harmonious living spaces that prioritize aesthetics and the well-being and vitality of occupants. The profound impact of biophilic design on our physical and mental health, as well as its potential to drive sustainability and innovation, cannot be overstated.
With each leafy wall, sun-soaked atrium, or artful incorporation of natural materials, architects and designers contribute to a tapestry of spaces that resonate with the rhythms of nature. Biophilic design invites us to reimagine our surroundings, nurturing a sense of tranquility, inspiration, and connection in the heart of urban landscapes.
As we embark on this journey toward a more sustainable, health-conscious, and visually captivating future, biophilic design principles serve as a guiding light. They remind us that amid our bustling cities and modern structures, the essence of nature can still thrive, providing a sanctuary for the soul and a testament to the enduring beauty of the natural world. So, let us embrace the allure of biophilic design, allowing it to shape our built environments and, in turn, improve our lives.
Biophillic Design
|
architects, architecture, built environments, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, enduring beauty, energy efficiancy, health-conscious, natural light, natural materials, natural world, nature, physiological benefits., sustainability, sustainable design
|
Architects are known for their creative and artistic abilities in designing beautiful and functional buildings, but they are also increasingly interested in the business and entrepreneurship aspects of their profession. As the architecture industry becomes more competitive and technology-driven, architects must develop a range of skills beyond design to succeed in the business world.
Architects who are interested in entrepreneurship are taking a proactive approach to grow their careers and building successful firms. They understand that business skills are essential for managing projects, attracting clients, and achieving financial stability. By developing an entrepreneurial mindset, architects can take advantage of new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
One key area of interest for architects is marketing. Architects who are skilled at marketing can effectively communicate their design vision to potential clients and stakeholders. They can also build their reputation and brand in the industry, which can lead to more business opportunities. Marketing can take many forms, from social media campaigns and website design to public relations and networking.
Financial management is another area of interest for architects who are interested in entrepreneurship. By understanding the financial aspects of running a business, architects can make informed decisions about project budgets, pricing, and cash flow. They can also develop strategies for managing risk and protecting their firm’s assets.
Project management is another area where architects can apply their business skills. Effective project management requires a range of skills, including communication, organization, and leadership. Architects who are skilled at project management can ensure that their projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the client’s satisfaction.
Finally, many architects are interested in innovation and technology. By keeping up with the latest advances in architecture and construction technology, architects can offer their clients cutting-edge solutions that are both efficient and sustainable. They can also leverage technology to streamline their business operations and improve their productivity.
In conclusion, architects who are interested in business and entrepreneurship are taking a proactive approach to build successful careers and firms. By developing a range of skills beyond design, including marketing, financial management, project management, innovation, and technology, architects can differentiate themselves in a competitive industry and offer their clients a range of valuable services.

Overall, an architect’s salary level has various factors playing a role, and architects must consider these factors when determining their earning potential.
The salary of an architect can vary widely depending on several factors, such as their experience, location, and the type of work they are engaged in. While some architects may earn lower salaries, there are several reasons why this may be the case:
- Supply and Demand: There are more architects than available positions, which can drive down salaries.
- Industry Competition: The architecture industry is highly competitive, and firms may be willing to hire less experienced architects at lower salaries.
- Project Budgets: Clients may have limited budgets for architectural services, which can result in lower fees for architects.
- Time and Effort: Architecture is a time-intensive profession that requires years of education and training. It can take a long time for an architect to become established and earn higher salaries.
- Public Perception: The public may not fully appreciate the value of architectural services, which can limit the amount that clients are willing to pay for them.
- Economic Factors: Economic downturns can also affect the demand for architectural services, reducing salaries in the field.
- Company Policies: No two firms’ compensation packages are alike. Choose a firm that wants to retain its employees over the long term and find a firm with good business acumen.
- Firm Size: Sole proprietors with one or two employees will deploy a different compensation package.
While architects certainly require artistic abilities to create beautiful and functional buildings, the success of an architectural practice also depends on its business acumen. Architecture firms must manage finances, attract clients, and navigate the legal and regulatory landscape like any other business.
Many successful architects are also skilled businesspeople. They understand how to market their services, manage finances, negotiate contracts, and navigate the industry’s complexities. They also have strong leadership and management skills, which are crucial for managing a team of professionals, overseeing multiple projects simultaneously, and building solid relationships with clients and contractors.
It’s worth noting that while artistic ability is a critical component of an architect’s skill set, it is not the only factor that determines their success. Good communication skills, problem-solving ability, attention to detail, and knowledge of technical requirements are also necessary. Additionally, architects must keep up with emerging technologies, sustainable design practices, and changing industry trends to remain competitive. In short, while artistic talent is essential to an architect’s skill set, successful architects must also have business acumen and leadership skills to thrive in their profession.

The salary of an architect can vary widely depending on several factors, such as their experience, location, and the type of work they are engaged in. While some architects may earn lower salaries, there are several reasons why this may be the case:
- Supply and Demand: There are more architects than available positions, which can drive down salaries.
- Industry competition: The architecture industry is highly competitive, and firms may be willing to hire less experienced architects at lower salaries.
- Project Budgets: Clients may have limited budgets for architectural services, which can result in lower fees for architects.
- Time and Effort: Architecture is a time-intensive profession that requires years of education and training. It can take a long time for an architect to become established and earn higher salaries.
- Public perception: The public may not fully appreciate the value of architectural services, which can limit the amount that clients are willing to pay for them.
- Economic factors: Economic downturns can also affect the demand for architectural services, reducing salaries in the field.
Overall, the salary of an architect can be influenced by various factors, and architects need to consider these factors when determining their earning potential. I know because I worked at several architecture firms before I started Consulting For Architects.
I am an artist, not a business expert.
While architects certainly require artistic abilities to create beautiful and functional buildings, the success of an architectural practice also depends on its business acumen. Architecture firms must manage finances, attract clients, and navigate the legal and regulatory landscape like any other business. Therefore, it is not necessarily true that architects are better artists than businesspeople.
Many successful architects are also skilled businesspeople. They understand how to market their services, manage finances, negotiate contracts, and navigate the industry’s complexities. They also have strong leadership and management skills, which are crucial for managing a team of professionals, overseeing multiple projects simultaneously, and building solid relationships with clients and contractors.
It’s worth noting that while artistic ability is a critical component of an architect’s skill set, it is not the only factor that determines their success. Communication skills, problem-solving ability, attention to detail, and knowledge of technical requirements are also necessary. Additionally, architects must keep up with emerging technologies, sustainable design practices, and changing industry trends to remain competitive.
In short, while artistic talent is certainly an essential aspect of an architect’s skill set, successful architects must also have business acumen and leadership skills to thrive in their profession.
Share your experience with me in the comment section, and I will respond.

In recent years, employees of architecture firms have increasingly attempted to join unions. This trend is driven mainly by the need for workers to protect and secure their rights as professionals. Unions provide a platform for employees to come together and negotiate fairer wages, better working conditions, and greater job security. Members can also access additional benefits such as legal advice, collective bargaining, and representation. Joining a union gives workers in the architecture field more control over their professional lives and helps to ensure that they are treated fairly and equitably by employers. As architectural firms continue to grow, the rights of employees must be protected and respected. Unions play an essential role in providing this protection, giving individuals the peace of mind that their rights and interests are protected.
By joining a union, architecture firm employees can help improve the industry. By negotiating better wages and working conditions, they can ensure that every professional in the field is treated fairly and compensated equitably for their work. The collective strength of union members also allows them to speak out against any injustices or exploitative practices they may experience, ensuring that their voices are heard and respected. With more people joining unions, the architecture industry is becoming safer and fairer for everyone involved.
Overall, union membership offers a range of benefits for employees in the architecture field. It gives them a platform to fight for their rights, negotiate better wages and working conditions, and ensure their voices are heard. By joining a union, they can help create a fairer and more equitable industry for everyone involved. As the architecture field continues to evolve, unions will remain essential to ensuring that workers’ rights are respected. But is it fools gold?
As architecture firm owners consider the implications of unionization, they must weigh the risks and rewards. Unionized firms face higher costs for labor, resulting in increased overhead that diminishes their competitive edge. Furthermore, collective bargaining agreements can restrict a firm’s ability to manage staffing levels and set salaries according to market conditions. Not being nimble can limit a firm’s ability to adapt quickly to changes in the industry, as well as its ability to attract and retain talented employees. Ultimately, these factors make unionization a less attractive option for many architecture firm owners. However, it is important to note that unions can bring tangible benefits, such as job security and improved wages and working conditions, which could appeal to some. Ultimately, it is up to individual owners to decide if unionization is the right choice for their businesses.
Architects are held to a high standard due to the critical nature of their work. They must possess excellent technical knowledge and communicate effectively with clients, designers, and contractors. As a result, they often require specialized training or certification to practice as professional architects. Despite this need for advanced skills and rigorous qualifications, architects are usually not eligible for collective bargaining, as many operate independently or in small firms and do not form unions. Thus, architects must advocate for their interests regarding workplace issues such as wages and working conditions. Architects must be aware of their rights and understand the profession’s regulations to ensure they receive fair compensation and working conditions. By doing so, architects can ensure they can continue practicing their craft in a healthy and productive environment.
Although architects traditionally do not form unions, they should still be aware of their rights and participate in the industry conversation around workplace issues. By doing so, architects can ensure they are compensated fairly and work in environments that promote their skillset and creativity. Architects must understand how their profession can benefit from unionization to better advocate for their interests.
It isn’t easy to find accurate statistics on how many architecture firms are unionized, as most are privately owned. However, there have been reports that suggest that under 3% of all architecture firms in the world and one firm in the United States may be part of a union or labor association.
Although becoming part of a union offers specific employee benefits, such as increased bargaining power and better wages, it can also be limiting in terms of flexibility. By joining a union, an architectural firm is subject to “just cause” guidelines regarding hiring and firing. Just cause means that there must be documented evidence that an employee is not meeting the standards of their position or has committed a punishable offense before they can be terminated. Therefore, it is complicated for an architectural firm to manage its workload most efficiently, as there may not be the flexibility to let go of employees quickly during times of low demand. Additionally, unions can restrict how many subcontractors or temporary workers an architecture firm can hire at any given time, limiting their ability to adapt to changing needs. Including dictating the workflow in contrast to increasing/decreasing staffing levels as needed. In addition, unions are not typically supportive of “at will” employment, which provides much more flexibility when hiring and firing.
Overall, unions can provide many benefits to architectural firms but also have certain restrictions that must be weighed carefully. Architecture firms must consider all their options before deciding on joining or not joining a union. Ultimately, the best solution will depend on each firm’s specific needs and goals.
For architecture firms that decide to join a union, there are measures they can take to ensure the best outcomes for their business. For example, firms should make sure they familiarize themselves with the rules and regulations of the union and negotiate any hiring or firing restrictions to ensure maximum flexibility when managing staff levels. Additionally, it is vital to understand the union’s grievance process and how disputes will be handled. Finally, firms should also consider creating a separate contract with the union that outlines their expectations for staffing levels and hiring and firing procedures.
By taking these measures, architectural firms can ensure that joining a union does not limit their ability to perform their work efficiently and effectively.
This information is for educational purposes and does not constitute financial, legal, or other professional advice. Please consult with a qualified professional if you require assistance.
Additional resources:
– New York Times: https://www.nytimes.com/2021/12/21/business/architects-white-collar-union.html
– The Real Deal: https://therealdeal.com/2022/09/01/new-york-firm-establishes-architectures-first-union/
– Architects’ Journal: https://www.architectsjournal.co.uk/news/do-architects-need-a-trade-union
– National Labor Relations Board (NLRB): https://www.nlrb.gov/
– American Institute of Architects (AIA): https://info.aia.org/join-aia/collective-bargaining-labor
– National Association of Architects (NAA): http://www.naahq.org/
– American Federation of Architects and Engineers: https://afae.org/
– Society of Professional & Executive Employers (SPEE): http://speeusa.org/
– U.S. Department of Labor: https://www.dol.gov/general/topic/labor-relations/labor-unions
– American Bar Association: https://www.americanbar.org/groups/labor_law/publications/aba_books/unionbargaining.html
– Harvard Law School: https://www.law.harvard.edu/news/labour/collective-bargaining-and-labor-unions/
– Cornell Law School: https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/labor_union
– Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS): https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2011/ted_20110429_data.htm
– Governing: https://www.governing.com/topics/workforce/unionizing-workers-collective-bargaining-rights.html
– National Labor Relations Board (NLRB): https://www.nlrb.gov/what-we-do/protecting-employee
Architecture Practice
|
architects, architecture, atwill, collectivebarganing, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, firing, Hiring, jobs, Jobsecurity, justcause, salary, Trade, Unions, wages, workingconditions
|
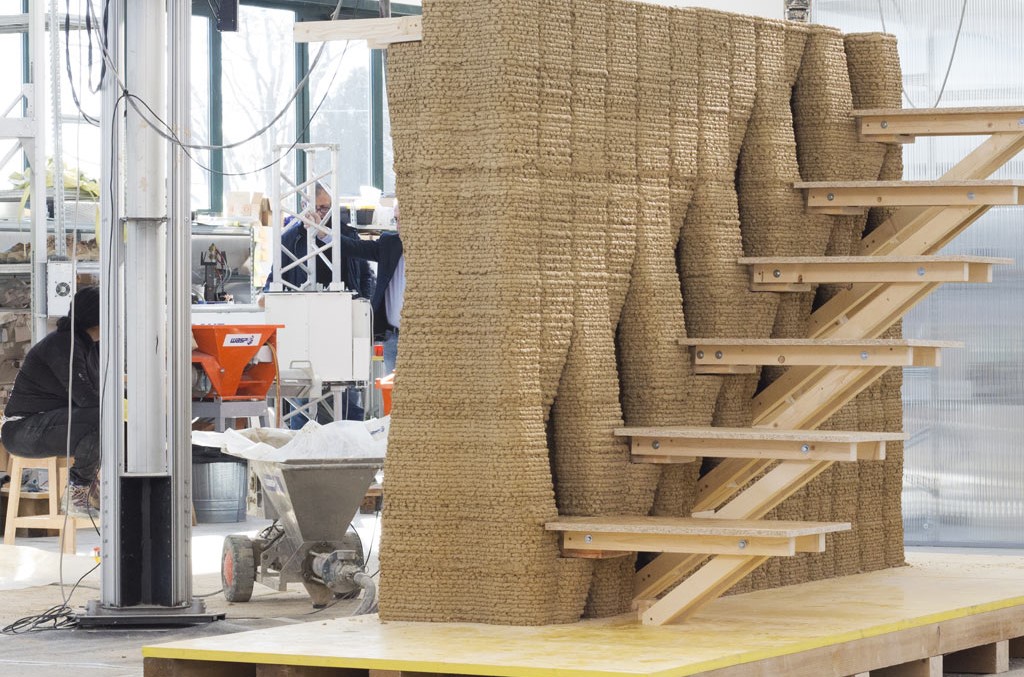

3D printing is revolutionizing the field of architecture, and it is poised to change the way we build our cities and towns in the future. Thanks to this innovative technology, we will be able to create more sustainable, resilient, and beautiful buildings than ever before.
In recent years, 3D printing has become increasingly popular, and it is now used in various industries. One area where 3D printing is making a significant impact is architecture. This technology offers several advantages for architects, including creating complex shapes and structures that would be impossible to create using traditional methods. 3D printing also allows for a high degree of customization, meaning that each architectural element can be designed to meet the project’s specific needs.
So how does 3D printing work in architecture? First, architects create a digital model of the desired structure using specialized software. Once the model is complete, it is sent to a 3D printer. The printer then creates the structure by building it up layer by layer, using materials such as plastic, metal, or concrete. This process can take anywhere from a few hours to several days, depending on the size and complexity of the project.
As anyone who has tried to put together a model kit can attest, 3D printing can be a great way to create complex shapes with high accuracy. Some of the world’s leading architecture firms are now using 3D printing to create scaled models of their proposed designs. Not only does this allow for greater precision in the planning stages, but it also allows for modifications to be made quickly and easily. In addition, using 3D printing means that architecture, engineering, and construction firms can create full-sized prototypes of their designs, which can be used to test the feasibility and identify any potential problems. As 3D printing technology advances, we will likely see more and more firms incorporating it into their design practices.
Several universities are now offering courses in 3D printing for architects. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in 3D printing among architects and other design professionals. As a result, several universities are now offering courses in this technology. These courses typically cover the basics of 3D printing, such as creating digital models and operating a 3D printer. In addition, students are often allowed to design and print their projects. These courses provide a great introduction to this exciting technology and its potential applications in architecture.
3D printing is set to change the way we build our cities. There is no doubt that 3D printing is a disruptive technology set to change how we build our cities. This technology offers several advantages for architects, including creating complex shapes and structures that would be impossible to create using traditional methods. In addition, 3D printing allows for a high degree of customization, meaning that each architectural element can be designed to meet the project’s specific needs. As the use of 3D printing technology continues to grow, we will likely see several innovative and exciting projects that push the boundaries of what is possible.
3D printing is a process that is constantly evolving and has the potential to change the landscape of architectural design. While there are some disadvantages to using this technology, the advantages often outweigh them. With continued advancement in 3D printing technology, we can only imagine what possibilities will be made available for architects and their clients. What do you think the future of 3D printing holds for architecture? Let us know in the comments below!
Related:
10 of the Best 3D Printers for Architects in 2022 Reviewed | Top Brands Compared
Reservations Begin in 2023 for the 100-home Community Codesigned by BIG-Bjarke Ingels Group
LGM turns to Quickparts for on-demand architectural modeling
Architecture Practice
|
3dmodel, 3dprinting, 3dsoftware, architects, architecture, Construction, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, digital, Engineering, jobs, model, project, technology
|
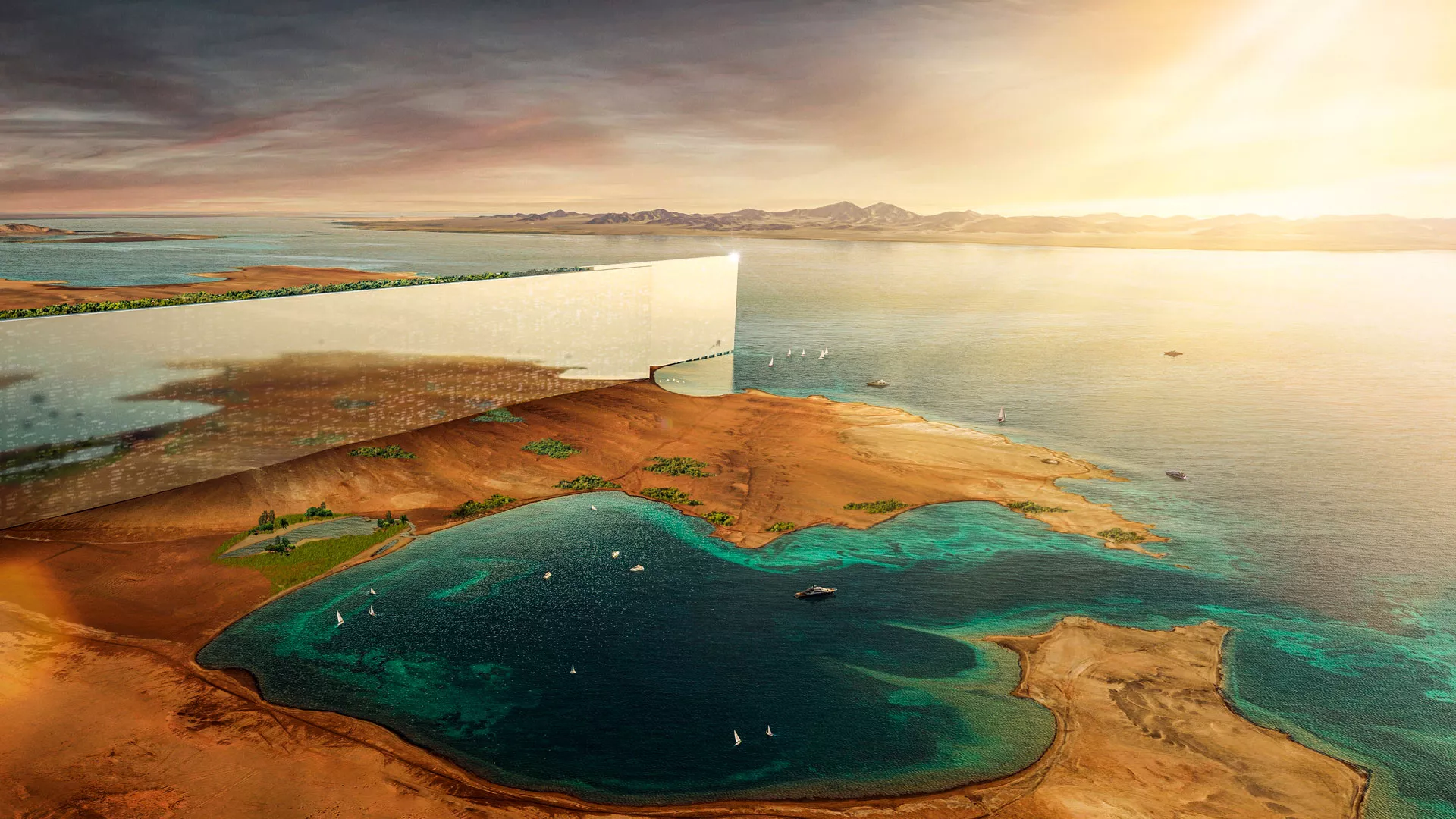

What started as a comment has become a short post in response to an opinion article by Adam Greenfield in the current edition of Dezeen online titled “All those complicit in Neom’s design and construction are already destroyers of worlds.”
In Sum.
• Adam Greenfield’s opinion article titled “All those complicit in Neom’s design and construction are already destroyers of worlds” argues that anyone who accepts money to work on any aspect of the Neom project is automatically complicit in everything that the project does.
• I disagree with this opinion. I believe that everyone is responsible for choosing which parts they work on and to what extent. If they are not comfortable with a particular aspect of the project, they can always decline to work on it or limit their involvement.
• Architecture is often seen as a symbol of power and authority, but it can also be seen as a reflection of the political and economic ideologies of the society in which it is built. In some cases, architecture may even help to shape these ideologies.
• The author paints architects who accept commissions with a broad brush when reality shows that many architects are conscious of ethical implications in their projects.
I disagree that if you accept money to work on any aspect of the Neom project, you need to know that you are complicit. I believe in and support many parts of the project, and I would gladly accept compensation for my work on those aspects. I do not think that taking money makes me automatically complicit in everything that the project does; it is my responsibility to choose which parts I work on and to what extent. If I am not comfortable with a particular aspect of the project, I can always decline to work on it or limit my involvement. Ultimately, it is up to each individual to decide whether or not they want to accept money to work on the Neom.
Architecture is often seen as a symbol of power and authority. This is especially true of traditional, classical architecture, which is often associated with authoritarian regimes such as the Roman Empire or the British monarchy. However, architecture is also drawn to capitalist and socialist governments. In capitalist societies, architecture is often seen as a way to make money and attract investment. In contrast, in socialist societies, it is seen as a way to improve the lives of citizens and promote equality.
Architecture can therefore be seen as a reflection of the political and economic ideologies of the society in which it is built. In some cases, architecture may even help to shape these ideologies. For example, the Bauhaus design school was founded in Germany in the 1920s to combine art and industry. This was when the country was undergoing a period of political and economic change, and the Bauhaus school helped shape the new German identity. Similarly, post-modern architecture emerged in the 1970s as a reaction to the modernist movement dominating architecture.
Noem’s cutting-edge Line project is about new tech and inventions to tackle global warming, setting a new benchmark for future urban cities. The developers and architects are a small part of the project team, which includes futurists, scientists, inventors, engineers, and artists. Their innovative approach means that the line project will not contribute to global warming but instead help fight it. This is a crucial step in the right direction. The Neom team is passionate about making a difference and ensuring that our planet has a bright future. We believe that through technology and innovation, we can make this happen.
The author paints the architects that accept commissions with a broad brush when the reality is much more nuanced. As such, it is essential to consider the ethical implications of their work. This includes whether or not they are contributing to the displacement of indigenous peoples or exacerbating climate change.
While it is easy to paint all architects and the commissions they earn with a broad brush, the reality is much more nuanced. Many architects are conscious of the ethical implications of their work and make an effort to minimize the negative impact of their projects.
It is essential to hold all architects accountable for the societal implications of their work. But it is also important to remember that not all architects are the same. Some are working to make a positive difference in the world. Knowing that sitting on the sidelines affects nothing Morphosis, Zaha Hadid Architects and other studios committed to the Neom project can sleep well tonight.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.
Op-Ed
|
AdamGreenfield, AllthosecomplicitinNeomsdesignandconstructionarealreadydestroyersofworlds, architects, architecture, bauhaus, business, cities, Consulting For Architects, David McFadden, design, dezeen, futurists, globalwarming, jobs, Line, Morphosis, Noem, Saudi, urban, zahahadid
|

As the gig economy continues to grow, so do the number of questions about how the law will be regulated. President Biden’s proposed legislation, the Protecting the Right to Organize (PRO) Act, includes several provisions that could significantly impact gig workers, including freelance architects and interior designers.
The PRO Act would make it easier for gig workers to unionize by clarifying that they are employees, not independent contractors. It would also give them the right to bargain collectively with their employers.
The bill would also make it illegal for companies to misclassify their workers as independent contractors to avoid paying benefits or complying with labor laws, even in cases where the worker is an independent contractor and prefers to work that way.
Working as an independent contractor has many benefits for architects and interior designers. These professionals can enjoy greater control over their work, schedule, and income. Additionally, they are not tied to one company or location and can take on projects that interest them from anywhere in the world. Independent contractors often have more freedom to negotiate fees and choose their working hours. They also typically have lower overhead costs than traditional businesses, which results in higher profits. In addition, they are not subject to the same employment laws and regulations as conventional businesses, giving them more flexibility in operating.
If you believe every worker in America should be the employee of a firm rather than work for themselves, you should support the passage of the PRO Act. If not, there are a few things that architects and interior designers can do to fight the passage of this law. First, they can educate themselves and others about the potential negative impacts of the law. Second, they can contact their local representatives and let them know their concerns. Finally, they can support organizations fighting against the passage of the law. Where do our professional associations stand? Contact the national headquarters of The American Institute of Architects and work with them to develop a strategy. https://www.aia.org/pages/6347502-federal-advocacy-outreach.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.

Flex-core staffing is an excellent way for architecture firms to break the hiring-firing cycle, increase their firm’s bottom line, and keep their employees happy. By hiring temp architects to fill in the peaks and valleys that always occur, firms can keep their core staff intact and avoid the need to engage and fire employees constantly. This practice can save firms both time and money, and it can also help them maintain a higher level of quality control.
Few things are more costly to a business than the hiring and firing cycle. Not only does it take a toll on your human resources department, but it can also significantly impact your bottom line.
Fortunately, there are ways to break the cycle and improve your financial situation. You can improve your bottom line and increase profits by taking some simple steps.
1. Review your hiring practices. Poor hiring practices are the most common causes of the hiring and firing cycle. If you’re constantly hiring and then firing employees, it’s time to take a closer look at your process. Are you screening applicants properly? Are you asking the right questions?
2. Train your managers. Another common cause of the hiring and firing cycle is poor management. If your managers constantly have to deal with employee issues, it’s time to give them some training. Teach them how to manage their teams and handle conflict appropriately.
3. Communicate with your employees. One of the best ways to avoid the hiring and firing cycle is to communicate with your employees. Let them know what your expectations are, and give them regular feedback. This will help them understand what they need to do to meet your standards.
4. Be consistent with your policies. You must comply with your policies to avoid the hiring and firing cycle. Make sure that everyone in your company knows your procedures and that they are followed. This will help to create a sense of stability and reduce the need for turnover.
5. Offer incentives. Another great way to avoid the hiring and firing cycle is to offer incentives for good performance. If you have employees who consistently meet or exceed your expectations, offer them a bonus or other incentive. This will show them you’re serious about their work and appreciate their efforts.
These simple steps can break the hiring and firing cycle and improve your bottom line. Implement these tips in your business today and see the difference it makes.
There are many ways to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line. One way is to increase the number of projects that the firm takes on. Another way is to increase the fees that the firm charges. Still, another method is to cut costs.
One way to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line is to increase the number of projects that the firm takes on. This can be done by marketing the firm more aggressively or by expanding the geographic areas that the firm serves.
Another way to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line is to increase the fees that the firm charges. This can be done by expanding the firm’s service rates or adding new services that command higher fees.
Still another way to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line is to cut costs. This can be done by streamlining the firm’s operations, eliminating unnecessary expenses, or finding ways to save on materials and labor.
Increasing an architecture firm’s bottom line can have many benefits. It can improve the firm’s financial health, allow the firm to hire more staff, and enable the firm to expand its services. Taking steps to increase an architecture firm’s bottom line can help the firm become more prosperous.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
After working at various design practices on a full-time and freelance basis and starting his design firm, David McFadden saw a gap to fill in the industry. In 1984, he created an expansive hub for architects and hiring firms to sync up, complete projects, and mutually benefit. That hub was Consulting For Architects Inc., which enabled architects to find meaningful design work while freeing hiring firms from tedious hiring-firing cycles. This departure from the traditional, more rigid style of employer-employee relations was just what the industry needed – flexibility and adaption to current work circumstances. David has successfully advised his clients and staff through the trials and tribulations of four recessions – the early ’80s, the early ’90s, the early 2000s, the Great Recession of 2007, and the Pandemic.
Hiring trends
|
architects, architecture, business, Consulting For Architects, design, employees, firing, firms, flex, Hiring, human, Interviewing, jobs, Labor Market, manage, porfolio, resources, resume, screening, staffing
|

















